CVSS Risk Assessment
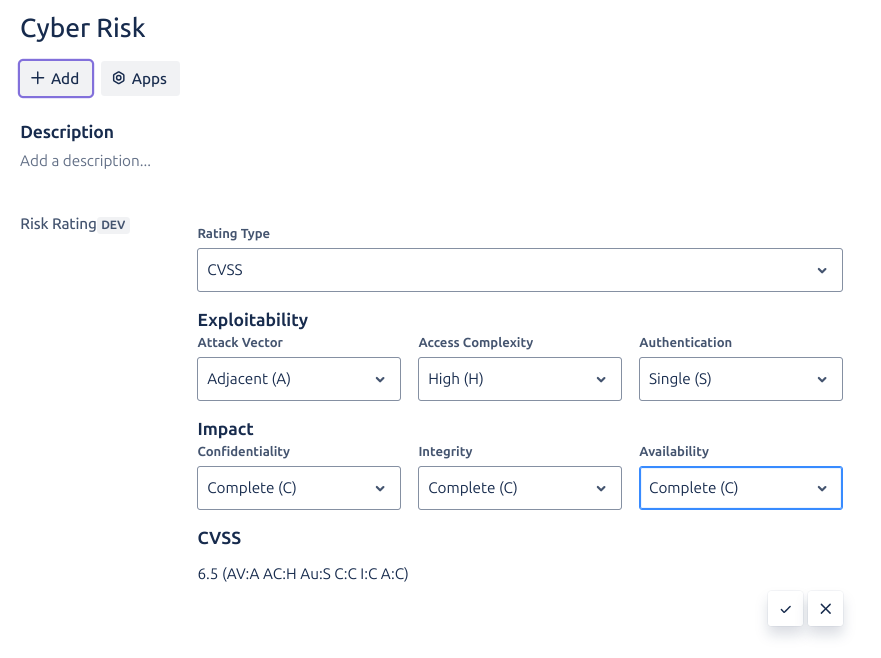
Use this type of risk ranking for assessing cybersecurity vulnerabilities in your medical device.
The CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) follows the BS EN ISO/IEEE 11073-40101:2022 standard for assessing and scoring security vulnerabilities. This mode provides a standardized approach to rating security risks based on several key metrics.
Input Metrics
The CVSS assessment consists of six base metrics:
- Attack Vector (AV): How the vulnerability is exploited. The more remote the attacker can be to attack a system, the greater the score.
- Network (N)
1.000: Attacker requires access to WAN or Internet. - Adjacent (A)
0.646: Attacker requires access to a broadcast or very short-range communications. - Local (L)
0.395: Attacker requires physical access to the device. - Undefined
0.000: N/A
- Network (N)
- Access Complexity (AC): The complexity of the attack required to exploit the vulnerability once an attacker has gained access to the system. The lower the required complexity, the higher the vulnerability score.
- Low (L)
0.710: Specialized access conditions or extenuating circumstances do not exist. - Medium (M)
0.610: The access conditions are somewhat specialized. - High (H)
0.350: Specialized access conditions exist. - Undefined
0.000: N/A
- Low (L)
- Authentication (Au): The strength of the authentication process used to exploit the vulnerability.
- None (N)
0.704: Authentication is not required to access and exploit the vulnerability. - Single (S)
0.560: Authentication is easily defeated or uses a weak method for vetting. Examples include:- Storing or transmitting of credentials in plain text
- Fixed (i.e., hard coded) credentials
- Automatic trust based on device type
- Multiple (M)
0.450: Authentication employs industry’s best practice for vetting the authenticity of the user or device. Examples include:- Storing of hashed credentials only
- Multiple levels of authentication
- Enforced unique credentials
- Undefined
0.000: N/A
- None (N)
- Confidentiality Impact (C): The impact to confidentiality of a successfully exploited vulnerability.
- None (N)
0.000: There is no impact to the confidentiality of the system. - Partial (P)
0.275: There is considerable information disclosure. Access to some system files is possible; however, the attacker does not have control over what is obtained, or the scope of the loss is constrained. - Complete (C)
0.660: There is total information disclosure, allowing all system files to be revealed. - Undefined
0.000: N/A
- None (N)
- Integrity Impact (I): The impact to integrity of a successfully exploited vulnerability.
- None (N)
0.000: There is no impact to the integrity of the system. - Partial (P)
0.275: Modification of some system files or information is possible; however, the attacker does not have control over what can be modified, or the scope of what the attacker can affect is limited. - Complete (C)
0.660: There is a total compromise of system integrity. - Undefined
0.000: N/A
- None (N)
- Availability Impact (A): The impact to availability of a successfully exploited vulnerability.
- None (N)
0.000: There is no impact to the availability of the system. - Partial (P)
0.275: There is reduced performance or interruptions in resource availability. - Complete (C)
0.660: There is a total shutdown of the target system, rendering the system’s principal functionality non-operational. - Undefined
0.000: N/A
- None (N)
Outputs
The CVSS mode generates two main outputs:
- CVSS Score: A numerical score from 0.0 to 10.0 representing the severity
- Vector String: A standardized representation of the selected metrics (e.g.,
AV:N AC:L Au:N C:P I:P A:P)
Default State
When creating a new CVSS assessment, all metrics are initially set to “Undefined” with:
- Score: 0
- Vector:
AV:? AC:? Au:? C:? I:? A:?
Using the Interface
- Select values for each of the six base metrics using the dropdown menus
- The CVSS score and vector string are automatically calculated and updated
- The field will indicate if mitigation is needed based on the calculated score
- You can track both initial and residual risk ratings
Best Practices
- Always provide values for all metrics - avoid leaving them as “Undefined”
- Consider the worst-case scenario when selecting impact values
- Document your reasoning for selected values in the issue comments
- Review and update the CVSS ratings as new information becomes available